For chlorination, paraffin wax should have low oil content (0.5%–1.5%), a stable melting point (58°C–64°C), and high purity.

Chlorinated paraffin waxes (CPWs) are produced by chlorination of straight-chained paraffin wax fractions. The carbon chain length of commercial chlorinated paraffin wax is usually between 10 and 30 carbon atoms, and the chlorine content is usually between 40 and 70% by weight. Chlorinated paraffin waxes are viscous colorless or yellowish dense oils with low vapor pressures, except for those of long carbon chain length with high chlorine content (70%), which are solid.
Chlorinated paraffin waxes are practically insoluble in water, lower alcohols, glycerol and glycols, but are soluble in chlorinated solvents, aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones, esters, ethers, mineral oils and some cutting oils. They are moderately soluble in unchlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons. Chlorinated paraffin wax consist of extremely complex mixtures, owing to the many possible positions for the chlorine atoms.
Applications of Chlorinated Paraffin Wax (CPW)
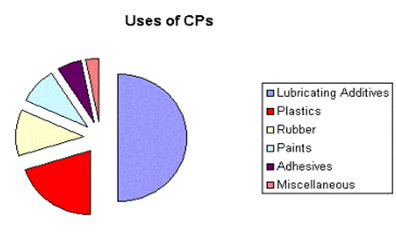
- CPW is used widely as a secondary plasticizer in flexible PVC compounds notably cable, footwear, hosing, conveyor belting, coated fabric and profiles. In these applications it can be used to partially replace more expensive primary plasticizers. In compounds with flame-retardant requirements, CPW is used to partially replace more expensive primary flame-retardants.
- An important benefit of CPW is its ability to reduce the unit cost of flexible PVC compounds. Correct reformulation with UNICHLOR produces PVC compounds with comparable physical properties: softness or hardness, tensile strength, elongation at break and others, as well as heat aged retention of physical properties.
- Increasingly, regulations specify flame resistance/ fire resistant in a growing number of applications. CPW is suitable for incorporation into PVC compounds and a range of other compounds and polymers, including polystyrene, polyethylene, polyester resins and natural and synthetic rubbers in products such as conveyor belts, polystyrene foam and glass fiber reinforced polyester.
- Textiles for carpets, carpet backing, tarpaulins and tents and Paints can be treated with compositions to induce flame retardancy.
- It is used in lubricants as an extreme pressure additive, where it forms a tenacious film on working parts. In cutting oils it is used as an additive to minimize ‘weld’ formation.
- In paints it is used as a plasticizer for binders and resins.
- It is also used in caulks and sealants.
- As an excellent carrier for powders such as pigments, stabilizers and inorganic fire retardants.
Supplier of Paraffin Wax for Chlorinated Industry
AT RAHA Paraffin Wax, We are paraffin wax supplier for Chlorinated Industry Across the world, we supply high-quality pharma petroleum jelly, tailored to meet the needs of various industries. However, our team will assist at every step to ensure a smooth and timely supply. (Contact Us)
Common Questions
1. What type of paraffin wax is used in the chlorinated industry?
In the chlorinated industry, manufacturers typically use fully refined or semi-refined paraffin wax with low oil content (0.5%–1.5%).
2. Why is paraffin wax important for producing chlorinated paraffin?
Paraffin wax is important for producing chlorinated paraffin because it acts as the primary raw material that undergoes chlorination.