Microcrystalline Wax

General description of microcrystalline wax
Sovereign’s Micro Crystalline Wax is white in color & has higher tensile strength & melting point. Because of its unique molecular structure, it is more branched and circular, resulting in an excellent adhesive.
Microcrystalline wax is a type of wax produced by DE-oiling petrolatum, as part of the petroleum refining process. Microcrystalline wax contains the high percentage of ISO paraffinic (branched) hydrocarbons and naphthenic hydrocarbons. It is characterized by the fineness of its crystals in contrast to the larger crystal of paraffin wax. It consists of high molecular weight saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons. Microcrystalline wax is generally darker, more viscous, denser, tackier and more elastic than paraffin waxes, and has a higher molecular weight and melting point. The elastic and adhesive characteristics of microcrystalline waxes are related to the non-straight chain components which they contain. The typical microcrystalline wax crystal structure is small and thin, making them more flexible than paraffin wax.
In contrast to paraffin, microcrystalline waxes may vary widely in character depending on the crude-oil source and the method and degree of refinement. Some are ductile, like beeswax; others are hard and brittle, and still others crumble easily during handling. The melting-point range is higher than that of paraffin wax, with commercial grades ranging from 63° to 93° C (145° to 200° F). The color of microcrystalline waxes ranges from creamy white to dark brown. Decolorization is difficult, and these waxes’ odor and taste may be undesirable in some applications.
How to Make Microcrystalline Wax
Microcrystalline waxes are derived from the refining of the heavy distillates from lubricant oil production. The product then must be DE-oiled at a wax refinery. Depending on the end use and desired specification, the product then may have its odor removed and color removed (which typically starts as a brown or dark yellow). This is usually done by means of a filtration method or by hydrotreating the wax material.
RAHA company guaranty the quality of Microcrystalline with the arrangement of the international inspector to check quality and quantity of the Microcrystalline during the loading to the vessel and controlling the production by QC by batch test report before shipping. RAHA Company guarantees the quality to meet with ASTM.
Categories and Applications of Microcrystalline Wax
Microcrystalline wax is commonly used in cosmetic formulations, glue manufacturing, and adhesives, skin care creams, inks, chewing gum, candles, rubber, gels, laminated paper products, in coatings and linings, in adhesives, sealing compositions, ointments and various types of polishes. It is also used in packaging & plastic industries.
Uses for Microcrystalline Wax in titles:
- Base for chewing gum, lipstick, cold creams, and ointments (where they harden, lubricate, carry additives, and protect against moisture)
- Food packaging, moisture proofing, film, foil, and corrugated board
- Increasing the fluidity and the flexible bonding of hot-melt adhesives
- Crayons, candles and caulk to sealants and fine polishes
- Host for compounds that prevent rust
- Insulating materials
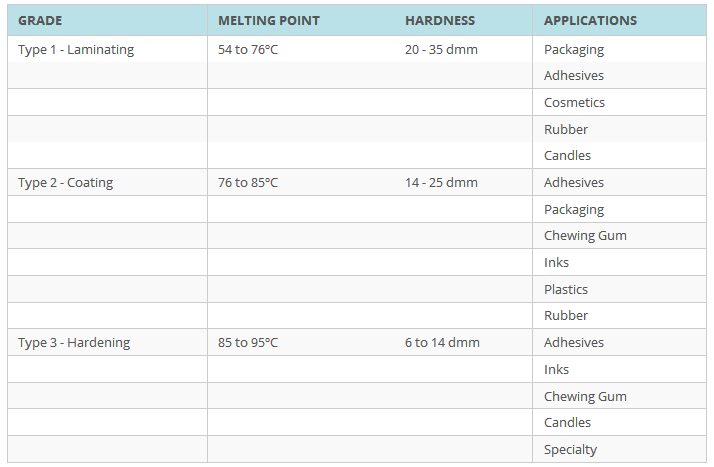
- Candle Additives (where they “bind” excessive oil or fragrances)Microcrystalline waxes may broadly be divided into 3 categories:
Microcrystalline Wax and Paraffin Wax Compared
Microcrystalline wax is a refined mixture of solid, saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons, and produced by de-oiling certain fractions from the petroleum refining process. Microcrystalline waxes differ from refined paraffin wax in that the molecular structure is more branched and the hydrocarbon chains are longer (higher molecular weight). As a result the crystal structure of microcrystalline wax is much finer than paraffin wax, and this directly impacts many of the physical properties. Microcrystalline waxes are tougher, more flexible and generally higher in melting point than paraffin wax. The fine crystal structure also enables microcrystalline wax to bind solvents or oil, and thus prevent the sweating-out of compositions.
| PARAFFIN WAX | MICROCRYSTALLINE WAX |
| Mainly unbranched alkanes | Mainly branched alkanes |
| Crystalline | Amorphous |
| Brittle | Malleable |
| Translucent | Opaque |
| Low melting (48 to 70ºC) | Higher melting (54 to 95ºC) |
| Glossy | Adhesive |
| Hard | Soft |
| White | White to colored |
| Odorless | Odorless |
Packing of microcrystalline wax
Microcrystalline wax is produced in 5 kg slabs which can be packed in carton or polypropylene bags and there is the possibility of palatalizing too.
Analysis of microcrystalline wax
| items | soft | hard | Test method |
| Oil content | 5-10 | 1% | ASTM D-721 |
| Flash point | 250 ˚c | 300 ˚c | ASTM D-92 |
| Color | Yellow | Cream | ASTM D-1500 |
| Melting point | 65±2 ˚c | 86-88 ˚c | ASTM D-87 |
| Congealing point | Approx 55 ˚c | 70 ˚c | ASTM D-3712 |
| Specific gravity | 0.8-0.82 gr/cm3 | 0.8-0.82 gr/cm3 | ASTM D-1500 |
| Kinematic viscosity | @100 ˚c approx 16 cst | @100 ˚c approx 16 cst | ASTM D-445 |